You may often hear the names PDF, Word, Excel, and PPT when people talk about the file types we use every day. Actually, people were constantly confused about which files had suffixes like -.doc, -.docx, -.xls, -.xlsx, and so on. This type of misunderstanding occurred more frequently while interpreting image file formats. Today, we’ll figure it out and explain to you when and how to use it. Continue reading.
A Clarification of Image File Formats (Use at the Right Time)
Image files are used in our daily lives in the same way that text files are. Everything, from the photographs on a restaurant menu to the sticker design printed, needs image files. It is critical to select the suitable image file format to ensure that the picture files handled by your software have the optimum quality and effect, like clearer, sharper, and more exquisite.
So for those with little experience in image processing, it can be generally sorted into 2 types of image files: Raster and Vector Images. The type you choose depends on your project and where the image will be used. Here’s an explanation.
Raster or Vector Images?
Related research in Images from the University of Michigan Library has indicated the difference between raster and vector images.
Raster Images
(aka bitmap images) consist of tiny pixels or dots. The resolution is defined and expressed in dpi. or dots per inch, for instance, 136 dpi equals 136 pixels per inch. The higher the dots per inch (dpi), the higher the resolution of the image.
Another point to clarify is that raster images have a fixed amount of pixels. For example, if we scale a raster image to enlarge it, without changing resolution, it will lose quality and look blurry or pixelated. This is because we are stretching the pixels over a larger area, thus making them look less sharp. JPEG/JPG, GIF, PNG, TIFF, and PSD are all raster images.
Vector Images:
(vector graphics) generally are made up of line art or path that can be infinitely re-size whether larger or smaller, for they work based on algorithms (take advantage of mathematical formulas to describe colors and shapes) rather than pixels, so one of the greatest things about vector images is that no increasing or decreasing in file size as clear as print out.
For example, a vector map poster could be stretched to fill the size of a wall without losing quality in the map’s texts, lines, and shapes. When you adjust the size of the vector map, the software will recalculate its shapes and colors through mathematical formulas to fit the new size. PDF, EPS, and AI files are vector images.
Now that you understand the difference between raster and vector images, let’s take a deeper look at the most often-used image file formats by category.
Raster image file formats (JPEG, RAW, GIF, PNG, TIFF, PSD)
JPEG/JPG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
Common image file specialized for storing photograph images. JPEG supports image compression that can delete the non-vital bits in the photos to reduce the file size as much as possible for saving space.
JPEG image file format is often used in the following cases:
- Digital camera, saving image files capable of multiple sizes.
- Files and documents, including Microsoft files and Open Office files, Powerpoint presentation files, and graphs.
- A website that could adjust the JPEG image file size to speed up page loading speed.
In addition, JPEG assists in storing up to 16 million colors, creating high-resolution and high-quality images suitable for both print and the web. However, the compression algorithm of JPEG reduces image quality every time the file is edited and saved.
For users who need to frequently edit and save images, JPEG may not be the best choice.
For most photography enthusiasts, JPEG is enough for their needs while professional photographers may prefer RAW format images.
RAW (Raw Image Formats for cameras)
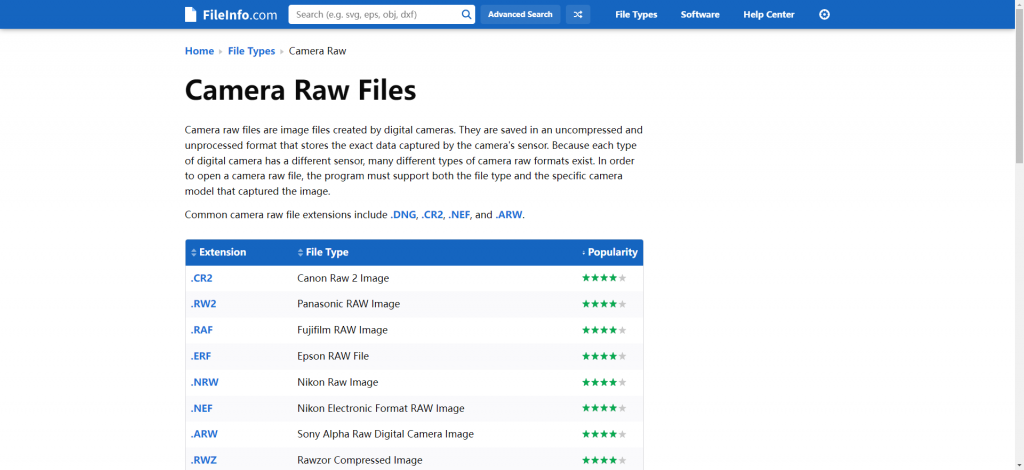
Common camera raw file extensions include -.DNG, -.CR2, -.NEF, and -.ARW.
RAW files contain the data that are uncompressed or are done with minimal processing, where those can accurately capture the content shot by the camera sensor meanwhile with no reduction in image quality. RAW image format is not as common as JPEG, here are the few file types that correspond to extensions:
- DNG: Apple ProRAW Image
- CR2: Canon Raw 2 Image
- NEF: Nikon Electronic Format RAW Image
- ARW: Sony Alpha Raw Digital Camera Image
- PEF: Pentax Electronic File Image
Literally, look at the explanation of each file type, RAQ is a kind of proprietary format that must be binding with a special camera model. In order to make it editable RAW files, the software must be compatible with the camera that took the photo. However, RAW images can go in need editing and storing many times without breaking the original image.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
GIFs are a common format for web graphics, especially small images, and images that contain text, such as navigation buttons or memes people love when chatting. A GIF comes from the combination of several separate image files together in order to create a single file, in other words, we always call the “several separate image files” picture frames. GIF files are saved in a lossless format, meaning that the GIF compression does not degrade the image’s clarity. Although the image quality will not be affected, it is not recommended to use GIF format in photographs, because it only contains 256 indexed colors at most.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNH file is a kind of bitmap image format with lossless compression, supports 256 grayscale levels, and 24-bit true color. Plus, a PNG image can choose the compression level when you output it, balancing the file size and image quality without any loss.
PNG format’s main application is to show up images on the Web or App in the form of logos, labels, buttons, or icons and the background of the website. People always use PNG to save a portrait or object with a transparent background as a cut-out material for merging with another picture.
The only thing that falls short is that PNG is always bigger than JPEG in file size. When transiting many images, consider the file size.
TIFF (Tagg Image File Format)
TIFF format belongs to the Raster image file that is popular with graphic artists and professional photographers as well as the standard of the printing industry. Because TIFF can preserve the metadata of the images in further details and color information without losing pixels.
The top advantage of TIFF is that it can be compressed or unzipped and allows bulk images stored in one single TIFF file, running in a smoother transfer despite it occupying much more than JPEG. I do not recommend using it on the web.
PSD (Photoshop Document)
PSD is the exclusive file format for Adobe Photoshop, it can store one or more than one piece of information that includes but is not limited to the image layers, transparency, text, layout, or other elements, thus PSD files are widely applied in many areas such as graphic design, photography, print, and digital art, among others.
But unfortunately, PSD could take a large file size which makes the less flexible, which means these kinds of files can only be opened and edited in limited software like Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Photoshop Elements, CorelDRAW, and Corel’s PaintShop Pro tool.
Vector image file formats (PDF, EPS, AI)
PDF (Portable Document Format)
PDF, developed by Adobe, is a powerful file format and is used worldwide. PDFs are accepted by numerous users for the reason that they offer excellent image quality, high-security, and can be viewed regardless of the hardware, software, and operating system that people use.
Apart from text and graphics, PDF file also comprises other elements like:
- Inserted video and audio files for dynamic presentation
- Spreadsheet and sheet data
- Bookmarks and Links
- Annotation and comments
- Forms and forms data
PDF plays a widespread use that can achieve cross-platform and device browsing as well as information sharing with coworkers. Moreover, different from other types of image files, PDF is able to make e-signature directly on the file easily viewed, you can try the PDF’s unique features by this one-class free online PDF tool (For example, ONEPDF) to make changes to it.

EPS (Encapsulated Postscript)
EPS is a format of vector image files primarily used for high-resolution printing of illustrations on PostScript printers and imagesetters. However, it can only be accessed through graphic software applications such as Adobe Illustrator or Corel Draw.
AI (Adobe Illustrator Document)
AI file format, utilized specifically by Adobe Illustrator, is frequently employed by graphic designers and regarded as the industry basis for generating images and artwork from nothing.
When to Use PDF Files Instead of Image Files
Though PDF has a large applying scope in practice, you may need to use PDF in such situations:
- Higher Security Required: PDF files cannot be modified or edited without leaving one’s fingerprints. In this way, PDF is quite useful for designers or entrepreneurs, or enterprises who want to guarantee safety and keep their privacy. PDF offers better security and it can be encrypted for deeper protection.
- More Stable File Needed: Using PDF can ensure the display of the content correctly being shown to whoever opens it or wherever people are using any operation systems.
- High-printing Quality and Convenience: PDF improves image quality when printing, for example, brochures and marketing materials, making it the preferred file type for many print stores. PDF file does not decrease the image quality during the process of converting to PDF, so don’t worry about the result will turn blurry or get details lost.
- Merging multiple images: If the image has been converted to PDF, thus can merge them into one single file. Concise the progress to send to others and drop the risk of overwhelmed attachments or files missing.
- Requirement to Control File Size: High-resolution images probably create a quite large file. With PDF format, avoid the problem of exceeding accessory size limits or taking up too much drive space. If the produced PDF size is still large, it can even be compressed appropriately until you feel satisfied.
Anyhow, the PDF format’s extensive application all due to its nailing points for high-image quality, guaranteed security, and regardless of any platforms, hardware, or device systems. What’s more, PDF files preserve the file format and layout to be the same as the original.
Here’s how to convert the following file formats using ONEPDF within seconds:
Learning the basics of managing image files to optimize workflow and increase productivity is not a difficult task. The guide above helps to figure out the different image file types in some aspects, guiding you to choose and use the right formats for your items going forward.Looking for a free, top-notch tool to manage your PDFs? Finding how ONEPDF can help you and what can ONEPDF do by converting, annotating, and e-signing online for more on our home page.